Table of Contents
What is “Scaling Up”?
“Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It…and Why the Rest Don’t” is a business book written by Verne Harnish. The book is a follow-up to his earlier work, “Mastering the Rockefeller Habits,” and it provides a comprehensive framework for growing and scaling a business successfully. Verne Harnish is a well-known expert in the field of business growth and has worked with numerous companies and entrepreneurs to help them expand their operations.
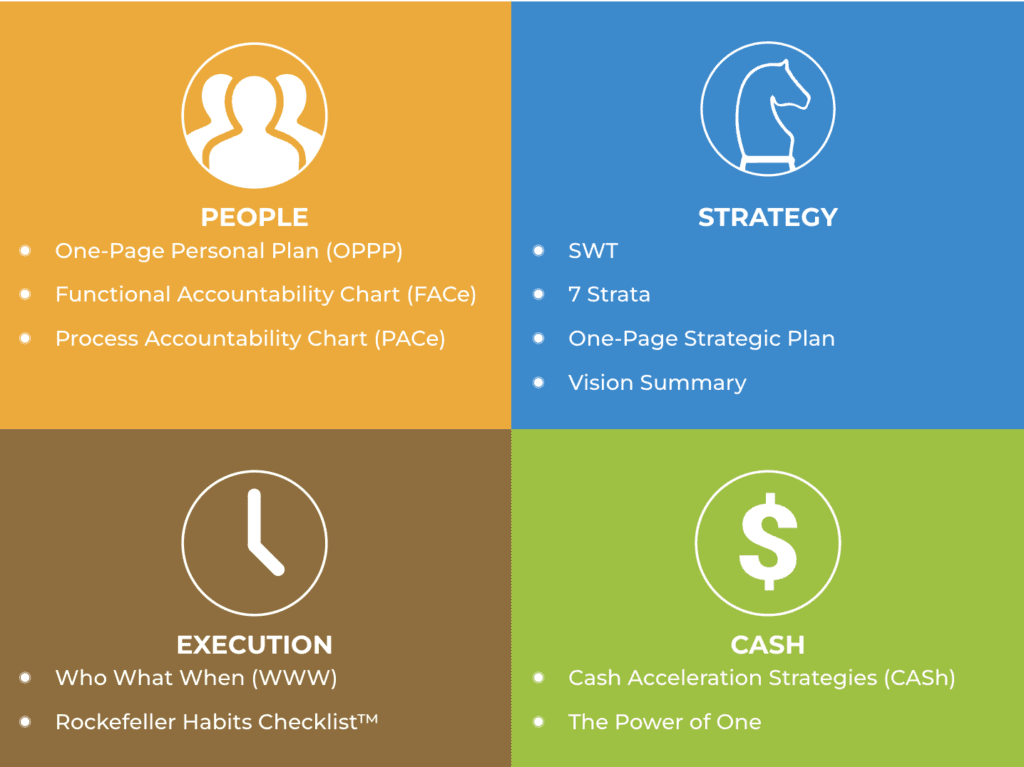
“Scaling Up” focuses on the four critical decisions that leaders and business owners need to make in order to drive business growth and scale effectively. These decisions are:
- People: Hiring and retaining the right people to build a high-performing team.
- Strategy: Developing a clear and effective strategy for the business.
- Execution: Ensuring that the strategy is effectively implemented.
- Cash: Managing the financial aspects of the business to support growth.
The book provides practical tools and advice for addressing each of these areas and offers insights into the common challenges and pitfalls that businesses face when trying to scale. It also emphasizes the importance of establishing a company culture and developing effective communication processes to align the entire organization with the growth objectives.
“Scaling Up” by Verne Harnish is widely used by business leaders, entrepreneurs, and management teams as a guide to achieving sustainable and profitable growth. It’s a valuable resource for those looking to take their businesses to the next level and navigate the challenges of scaling.
People
The first critical decision is “People.” This decision focuses on the pivotal role that hiring and retaining the right individuals plays in building a high-performing team within an organization. Effective teams are the cornerstone of business success, and selecting and keeping the right people is essential for achieving sustainable growth and long-term success.
Key Concepts
a. Talent Identification and Acquisition: In “Scaling Up,” Verne Harnish emphasizes the importance of identifying and acquiring top talent. This process involves seeking individuals who not only have the necessary skills and experience but also align with the company’s values and culture. Hiring the right people requires a thorough and strategic approach, including targeted recruitment, interviewing techniques, and thorough reference checks.
b. Culture Fit: Ensuring that new hires align with the company’s culture is a central concept. A strong cultural fit ensures that employees are more likely to embrace the company’s values, vision, and goals, leading to greater motivation and teamwork.
c. Retention Strategies: Retaining valuable employees is equally important. “Scaling Up” provides insights into various retention strategies, including competitive compensation, professional development opportunities, and creating a positive work environment that fosters engagement and loyalty.
d. Alignment with Core Values: Core values are at the heart of “People” in “Scaling Up.” Ensuring that team members share and uphold these values contributes to a cohesive and productive team dynamic.
e. Team Development: The book suggests investing in team development and continuous learning to enhance skills and foster collaboration. Building high-performing teams is not solely about hiring but also about nurturing and evolving existing talent.
Examples
a. Netflix: Netflix is a prime example of a company that has successfully built high-performing teams. They are known for their unique and effective hiring practices, particularly their culture deck, which outlines their core values and expectations. This culture-focused approach has enabled Netflix to attract individuals who resonate with their values, contributing to a dynamic and high-performing workforce.
b. Zappos: The online retailer Zappos is renowned for its dedication to cultural fit. They offer new hires $2,000 to leave the company after the initial training if they feel that the company culture isn’t right for them. This approach not only attracts those who genuinely align with Zappos’ values but also underscores the importance of culture in team building.
c. Google: Google is known for offering numerous perks and professional development opportunities to its employees. They invest in retaining their workforce by creating an environment where employees are encouraged to innovate and continuously improve their skills. This commitment to employee development has contributed to Google’s success in building high-performing teams.
In summary, the “People” component in “Scaling Up” underscores the critical role of hiring and retaining the right individuals in building high-performing teams. It emphasizes talent acquisition, cultural alignment, retention strategies, core values, and continuous team development as key concepts for success. By implementing these principles, organizations can cultivate strong teams that drive growth and adapt to the ever-evolving demands of the business world.
Strategy
The second critical decision is “Strategy.” This decision is a fundamental pillar for any business aiming to achieve sustainable growth and prosperity. “Strategy” in “Scaling Up” is all about developing and implementing a well-defined, effective plan that guides the organization towards its goals and helps it navigate through the complexities of the business landscape.
The “Strategy” decision in “Scaling Up” underscores the importance of having a well-defined, adaptable plan that guides an organization toward its goals. Key concepts include vision and goals, SWOT analysis, prioritization, execution, and feedback and adaptation. These concepts are exemplified by companies like Apple, Amazon, and Southwest Airlines, which have successfully implemented clear and effective business strategies to achieve their objectives and sustain growth.
Key Concepts
a. Vision and Goals: A successful business strategy starts with a clear vision and well-defined objectives. Verne Harnish emphasizes that leaders must articulate the company’s long-term vision and establish specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
b. SWOT Analysis: Conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) is a critical concept. This analysis helps businesses assess their internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats, enabling informed decision-making.
c. Prioritization: In “Scaling Up,” Verne Harnish highlights the significance of prioritization. Leaders must focus on the most impactful strategies and avoid getting bogged down in non-essential activities. Effective prioritization ensures that resources are allocated where they will have the most significant impact.
d. Execution and Accountability: Strategy without execution is merely a plan on paper. “Scaling Up” emphasizes the importance of execution and accountability, with a focus on setting clear responsibilities and holding individuals and teams accountable for their roles in strategy implementation.
e. Feedback and Adaptation: An effective strategy is dynamic, not static. It evolves based on feedback, changing market conditions, and emerging opportunities. Organizations must be agile and willing to adapt their strategies to stay relevant and competitive.
Examples
a. Apple Inc.: Apple’s strategy is a prime example of a clear and effective business strategy. Their vision of making technology accessible and user-friendly has guided them to create innovative and sleek products. They prioritize design, customer experience, and a closed ecosystem to build a loyal customer base. The company’s strategic focus on developing both hardware and software has resulted in a highly successful and integrated product lineup.
b. Amazon: Amazon’s strategy has been based on long-term thinking and customer-centricity. Their vision is to be the “Earth’s most customer-centric company,” and they have executed this strategy by continuously expanding their product and service offerings. They have prioritized efficiency and customer satisfaction, using data-driven decision-making to adapt to changing market conditions.
c. Southwest Airlines: Known for its cost leadership strategy, Southwest Airlines provides an example of a well-executed strategy. Their focus on offering low-cost, no-frills air travel has allowed them to grow and maintain profitability. They prioritize quick turnaround times at the airport, point-to-point routes, and a no-baggage-transfer policy.
Execution
In Verne Harnish’s book “Scaling Up,” the third critical decision is “Execution.” This decision focuses on the crucial process of translating a well-defined business strategy into action. Effective execution is the linchpin between strategy development and achieving desired business outcomes. It involves making the strategic plan a living reality within the organization.
The “Execution” decision in “Scaling Up” underscores the importance of effectively translating strategy into action. Key concepts include clear communication, accountability, KPIs, continuous improvement, and regular rhythms. Successful execution is exemplified by companies like GE, Toyota, and Walmart, which have achieved their strategic objectives through rigorous and effective execution processes.
Key Concepts
a. Clear Communication: Successful execution begins with clear communication. Verne Harnish emphasizes that leaders must effectively communicate the strategy to all levels of the organization. When employees understand the strategy and their role in executing it, they are more likely to align their efforts with the company’s objectives.
b. Accountability: Accountability is a central concept in execution. Leaders need to assign clear responsibilities and hold individuals and teams accountable for achieving their goals. This involves setting expectations, tracking progress, and providing feedback.
c. KPIs and Metrics: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics are vital for monitoring and measuring progress. Verne Harnish encourages the use of specific, measurable, and time-bound metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of the strategy execution. These metrics provide a basis for data-driven decision-making.
d. Continuous Improvement: Effective execution is not static; it’s an ongoing process. Verne Harnish stresses the importance of continuous improvement and adaptation. Organizations must learn from their experiences, adjust their approaches, and stay agile in the face of changing market conditions.
e. Rhythms and Meetings: The book advocates for the establishment of rhythms and regular meetings to maintain alignment and ensure that execution stays on track. These meetings provide a forum for discussing progress, addressing challenges, and making necessary course corrections.
Examples
a. General Electric (GE): GE is a notable example of a company that has emphasized execution as a core principle of its success. Under former CEO Jack Welch, GE became known for its rigorous performance reviews, which led to the “rank and yank” practice, where the lowest-performing employees were removed. This intense focus on accountability and execution helped drive significant growth during Welch’s tenure.
b. Toyota: Toyota’s execution excellence is a key factor in the company’s sustained success. The “Toyota Production System” is renowned for its focus on lean manufacturing, continuous improvement, and employee engagement. The system emphasizes error detection and correction, which contributes to high product quality and efficient execution of production processes.
c. Walmart: Walmart’s execution strategy is centered around delivering everyday low prices to its customers. The company’s logistical prowess ensures that products are stocked efficiently, resulting in cost savings and competitive pricing. Walmart also uses performance metrics and data-driven decision-making to track progress and adapt its execution strategies.
Cash
In “Scaling Up” by Verne Harnish, the fourth critical decision is “Cash.” This decision underscores the critical importance of managing the financial aspects of a business to enable and support its growth. Effective cash management is the lifeblood of an organization, and it plays a central role in achieving and sustaining business success.
Maastering Cashflow highlights the pivotal role of financial management in supporting business growth. Key concepts encompass cash flow management, financial forecasting, cash conversion cycles, cash reserves, and debt management. Companies like Apple, Amazon, and Berkshire Hathaway demonstrate how effective cash management can create the financial stability and flexibility needed to pursue growth opportunities while maintaining the financial health of the business.
Key Concepts
a. Cash Flow Management: Managing cash flow is the heart of this decision. Harnish emphasizes the need to have a clear understanding of the company’s cash inflows and outflows. It’s about ensuring that more cash comes in than goes out and maintaining sufficient liquidity to cover expenses and investments.
b. Financial Forecasting: Effective financial forecasting is crucial. Companies must create accurate forecasts that project future cash needs, enabling them to anticipate and address potential shortfalls before they become critical. This involves monitoring cash flow on a regular basis, not just during financial crises.
c. Cash Conversion Cycle: Reducing the cash conversion cycle is another key concept. Harnish suggests minimizing the time it takes to turn investments (in inventory, labor, etc.) into cash receipts. This reduces the need for large cash reserves, freeing up capital for other growth initiatives.
d. Cash Reserve and Contingency Planning: While it’s vital to invest in growth, maintaining a cash reserve is equally important. Having a safety net for unexpected expenses or economic downturns ensures that the business can weather storms without sacrificing growth plans. Contingency planning helps the business navigate financial challenges effectively.
e. Debt Management: Effective debt management is crucial. Businesses need to balance their use of debt for expansion while not overleveraging themselves. Harnish discusses how to optimize debt to fuel growth without creating financial instability.
Examples
a. Apple: Apple is a case study in effective cash management. The company has amassed a significant cash reserve, which it uses for strategic acquisitions, research and development, and other growth initiatives. Apple’s strong cash position gives it the flexibility to make long-term investments without compromising day-to-day operations.
b. Amazon: Amazon is known for its focus on maintaining low cash conversion cycles. The company has developed efficient supply chain and inventory management systems that enable it to turn inventory into revenue quickly. This approach minimizes the need for extensive cash reserves while supporting rapid growth.
c. Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway: Berkshire Hathaway’s founder Warren Buffett is known for his approach to cash management. He keeps substantial cash reserves, allowing the company to seize investment opportunities when they arise, even during market downturns. This strategy highlights the importance of maintaining cash liquidity for long-term growth.
Additional Reading
- “Good to Great” by Jim Collins: This classic business book explores why some companies make the leap from good to great and sustain excellence over time. It offers valuable insights into what it takes to build enduring, successful organizations.
- “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries: Eric Ries provides a methodology for developing businesses and products in an environment of extreme uncertainty. The book is a valuable resource for entrepreneurs and leaders looking to build scalable and sustainable businesses.
- “Built to Last” by Jim Collins and Jerry I. Porras: Another work by Jim Collins, this book examines the habits and characteristics of visionary companies that have endured and outperformed their competitors over the long term.
- “Blue Ocean Strategy” by W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne: This book offers a framework for creating uncontested market space and making competition irrelevant. It focuses on innovation and strategic thinking to discover new opportunities.
- “Lean Thinking” by James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones: Building on the principles of lean manufacturing, this book outlines how to apply lean thinking to various aspects of a business, with a strong emphasis on efficiency and value creation.
- “The Innovator’s Dilemma” by Clayton Christensen: Christensen’s book explores why successful companies can fail, as well as the concept of disruptive innovation. It offers insights into the challenges of sustaining innovation and growth.
- “Start with Why” by Simon Sinek: Sinek delves into the importance of starting with a clear “why” when it comes to leadership and business strategy. He argues that companies that understand and communicate their “why” are more likely to inspire and succeed.
- “The Art of Strategy” by Avinash K. Dixit and Barry J. Nalebuff: This book provides a comprehensive overview of various aspects of strategy, including game theory, negotiation, and decision-making. It’s a valuable resource for strategic thinking and planning.
- “Competitive Strategy” by Michael E. Porter: Michael Porter’s classic work on competitive strategy delves into the five competitive forces that shape strategy and how organizations can gain a sustainable competitive advantage.
- “Great by Choice” by Jim Collins and Morten T. Hansen: In this book, Collins and Hansen examine why some companies thrive in uncertain environments while others do not. They explore the role of leadership, innovation, and discipline in achieving long-term success.
