Table of Contents
What is the McKinsey 7S model?
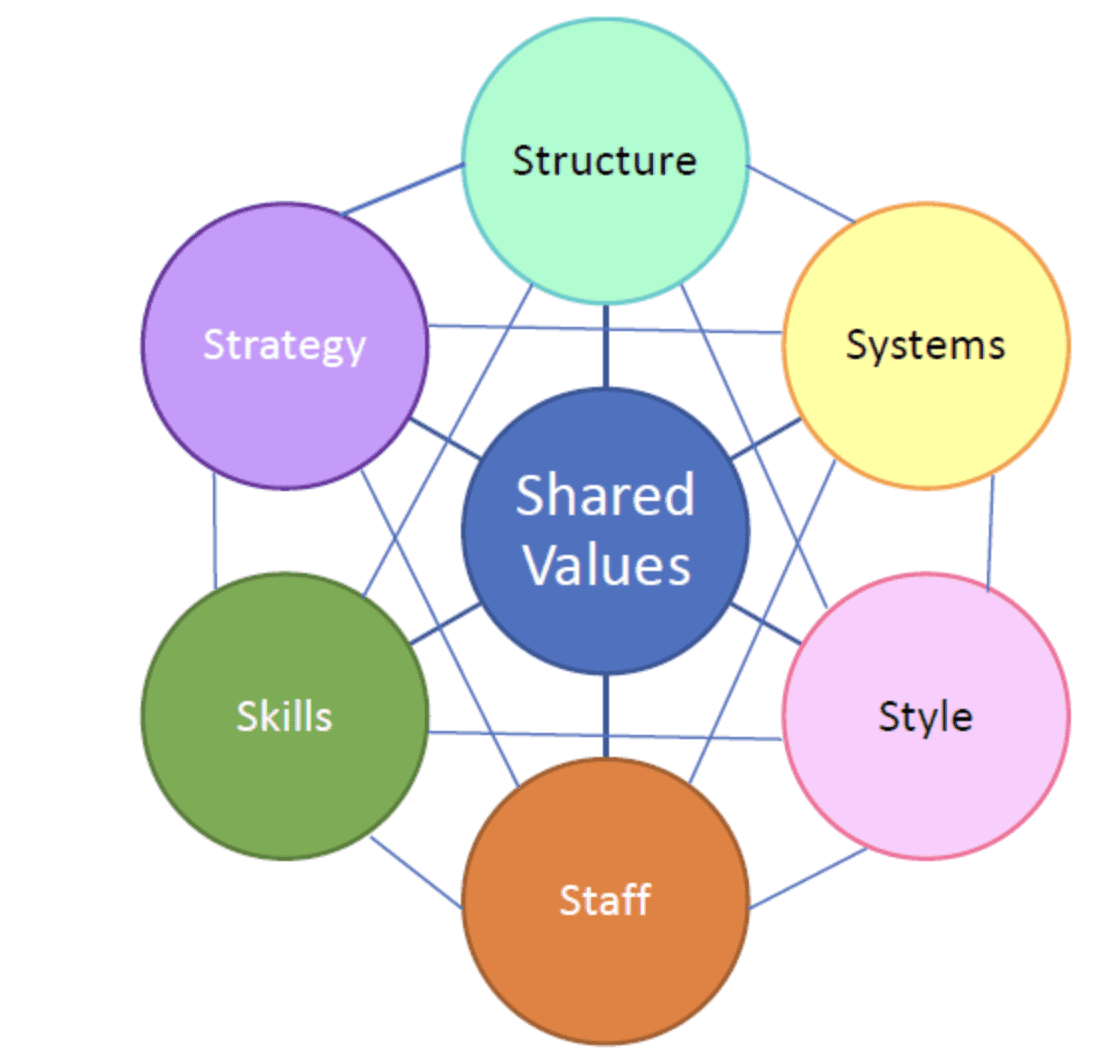
The McKinsey 7-S Model is a management problem solving framework used to assess and improve organizational effectiveness and performance. It was developed by management consultants at McKinsey & Company and focuses on seven key internal elements that need to be aligned for an organization to function effectively. These elements are divided into “hard” and “soft” factors:
Hard Elements (Easily Identifiable and Influenced):
- Strategy: The organization’s plan for achieving its goals.
- Structure: The organizational structure and hierarchy.
- Systems: The processes and procedures in place.
Soft Elements (Culture and Values): 4. Shared Values: The core beliefs and values that guide behavior. 5. Skills: The collective abilities and competencies of the workforce. 6. Style: The leadership and management style within the organization. 7. Staff: The employees and their competencies.
The 7-S Model helps organizations analyze their current state and identify areas where alignment is needed to improve performance and implement change effectively. It’s commonly used in strategic planning, change management, and organizational design.
How does it work?
The McKinsey 7-S Model works by assessing and aligning seven key internal elements within an organization to improve its effectiveness and performance. Here’s how it works:
- Identify the Seven Elements: The first step is to identify and understand each of the seven elements within your organization: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, and Staff. These elements encompass both “hard” (tangible) and “soft” (cultural) aspects of the organization.
- Assess the Current State: Evaluate the current state of each of these elements. This involves gathering data, conducting interviews, and analyzing documents and processes to understand how each element is functioning within the organization.
- Alignment Analysis: The key concept in the 7-S Model is alignment. Assess how well these seven elements are aligned with each other. For example, check if your strategy aligns with your organizational structure, or if your leadership style is consistent with your shared values.
- Identify Misalignments: During the analysis, you may identify misalignments or areas where elements are not congruent with each other. These misalignments can be sources of inefficiency, conflict, or poor performance within the organization.
- Set Objectives: Determine what the desired state of alignment should be. What changes or improvements are needed in each element to better align them with the others and with the organization’s goals and objectives?
- Develop Action Plans: Create action plans to address the identified misalignments. These plans may involve changes in strategy, restructuring the organization, implementing new systems, or fostering a specific organizational culture.
- Implement Changes: Put the action plans into practice. This often involves working with various departments and teams to execute the necessary changes. Effective communication and leadership are essential during this phase.
- Monitor and Adapt: Continuously monitor the progress of the changes and make adjustments as needed. The alignment of these elements is an ongoing process, and the organization may need to adapt to external factors or evolving goals.
- Measure Results: Assess the impact of the changes on organizational performance. Have the improvements led to better efficiency, productivity, and overall success? Measurement helps in understanding the effectiveness of the alignment efforts.
- Iterate and Refine: Based on the results and feedback, iterate and refine the alignment efforts. The 7-S Model is a flexible framework that can be applied iteratively as the organization evolves. See Investopedia for more detail.
Example
Let’s apply this model to a Chocolate shop called “Choc-Box”.
- Strategy (S1 – “What’s on the Menu”): In this case, the strategy represents the chocolate shop’s menu. The shop decides to focus on offering a wide variety of chocolate types, including vegetarian, meat lovers, and gluten-free options. This is the core plan for achieving its business goals.
- Structure (S2 – “Kitchen Layout and Staffing”): The organizational structure refers to the physical layout of the shop and its staffing. The shop has a small kitchen area and a team of three cooks. This is how the resources are organized to execute the strategy.
- Systems (S3 – “Ordering and Delivery Process”): Systems encompass the processes and procedures in place. The chocolate shop has an efficient online ordering system, a delivery process that ensures hot chocolates reach customers on time, and a well-organized kitchen workflow.
- Shared Values (S4 – “Customer Satisfaction”): Shared values represent the core beliefs and values that guide behavior. The chocolate shop values customer satisfaction above all else. This shared value drives decisions, such as using high-quality ingredients and providing excellent customer service.
- Skills (S5 – “Culinary Expertise”): Skills refer to the collective abilities and competencies of the workforce. The chocolate shop hires experienced chocolate chefs who are skilled in making delicious chocolates. This aligns with their strategy of offering high-quality chocolates.
- Style (S6 – “Friendly and Welcoming Atmosphere”): Style relates to the leadership and management style within the organization. The chocolate shop’s style is to create a friendly and welcoming atmosphere for both customers and employees. This aligns with the shared value of customer satisfaction.
- Staff (S7 – “Hiring and Training”): Staff includes the employees and their competencies. The chocolate shop carefully selects and trains staff to ensure they can prepare chocolates to the shop’s standards and provide excellent customer service.
Analysis: Now, let’s analyze how the 7-S elements align:
- The strategy (menu variety) aligns with the structure (small kitchen and three cooks) because the menu can be efficiently prepared with the available resources.
- The systems (ordering and delivery) are aligned with the strategy (customer satisfaction) because they ensure timely deliveries and excellent service.
- The shared value (customer satisfaction) aligns with the skills (culinary expertise) and style (friendly atmosphere) because they contribute to creating a positive customer experience.
- The staff (trained employees) aligns with the shared value (customer satisfaction) as they play a crucial role in delivering excellent service.
Improvements: Suppose the chocolate shop identifies a misalignment where customer feedback indicates long delivery times. In this case, the shop could adjust its systems (S3) by optimizing delivery routes or increasing the number of delivery drivers to better align with the shared value of customer satisfaction (S4). By using the McKinsey 7-S Model, the chocolate shop can continually assess and adapt its elements to maintain alignment with its strategy and values, ultimately leading to a successful and customer-centric business.
References:
- xxx